
Fossil fuel-derived synthetic fibers, which are nonrenewable and nonbiodegradable, currently comprise approximately 60% of materials used by the fashion, automotive, and home goods industries and are projected to comprise approximately 70% of materials by 2030. Synthetic materials contain microplastics, which accumulate and persist in ecosystems for hundreds of years, as well as toxins that poison ecosystems, harm animals, and fuel climate change.
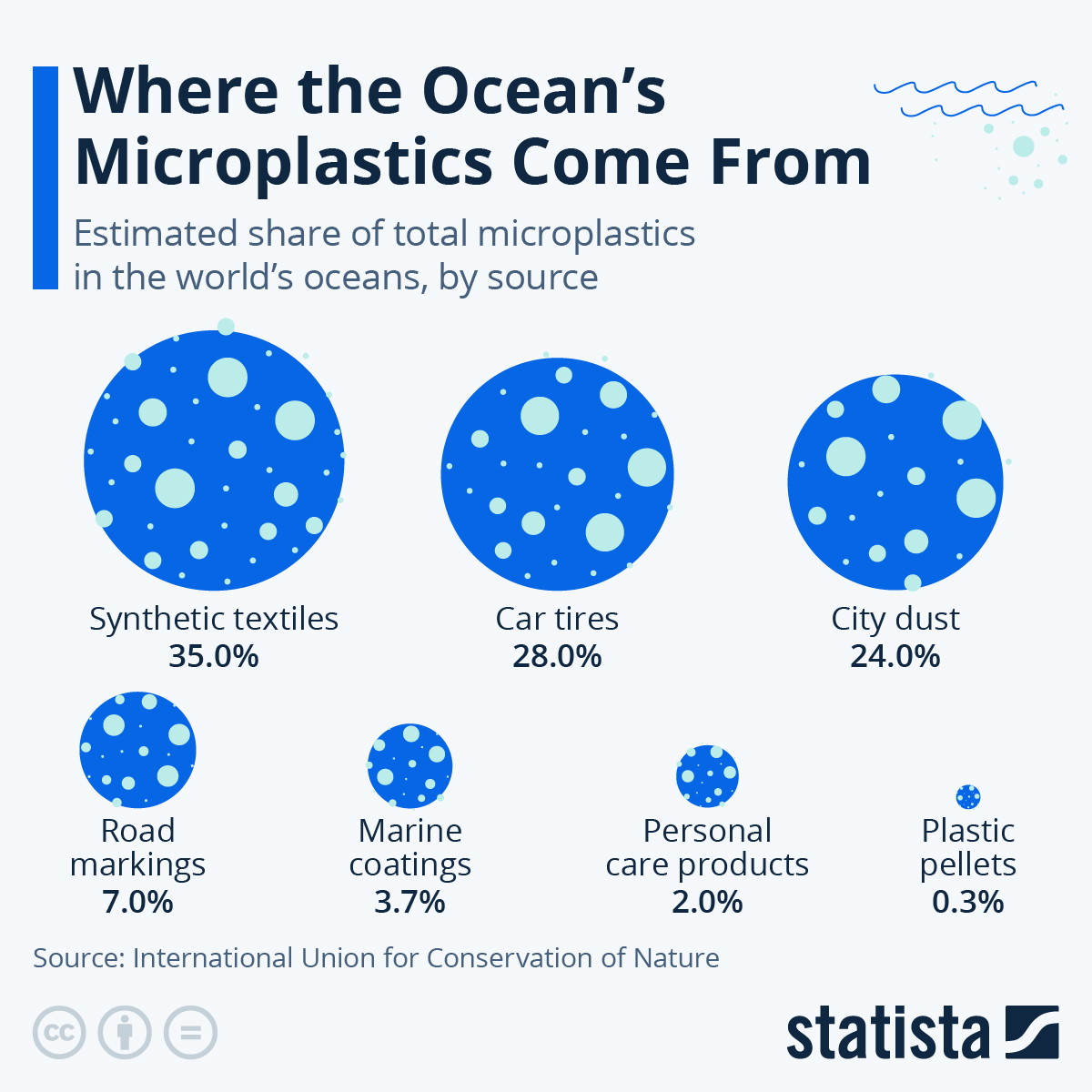
According to the IUCN, synthetic textiles are the number one source of microplastics in oceans (Statista, 2022)
MII’s Impact of Synthetic Materials on Animals report finds that synthetic materials must be replaced with sustainable and humane next-gen materials for the health of our planet and future generations.
Want to learn more about our research? Browse our reports page.
